What language is spoken in Cambodia?

Khmer Language - Cambodian Language
The Official Cambodian Language is Khmer. In Cambodia, Khmer is the official language and spoken by nearly 90% of the population. However, there are several different languages that constitute the country’s vast linguistic system. In this article, we will help you to answer the question: What language is spoken in Cambodia?
1. The Official Language of Cambodia
Khmer, also known as Cambodian, is the most popular language in Cambodia and is by far known as the single official language and used in most social and professional contexts such as government administration, all levels of education, and social media.

The Official Language of Cambodia is Khmer
After Vietnamese language, Cambodian Language is the second most widely spoken Austroasiatic language* in the world, with approximately 16 million speakers.
(* The Austroasiatic languages, also known as Mon–Khmer, are a large archaic language family in areas stretching from the Malay Peninsula through Southeast Asia to East India. Of these languages, only Khmer in Cambodia and Vietnamese in Vietnam have official status as modern national languages – more information here).
Khmer has been considerably influenced by Sanskrit and Pali, particularly in the royal and religious registers. These two languages originated from ancient India and were introduced in Cambodia through the religions of Hinduism and Buddhism. Due to geographical proximity and long-term cultural contacts with the native speakers of Vietnamese, Chinese, Thai, Lao, and Cham, the regional dialects of Khmer also have been influenced by these languages. Central Khmer is spoken by the vast majority of Khmer speakers. Because it is the dialect from the central plain where the Khmer are most heavily concentrated.

Khmer (also known as Cambodian Language) is the single official language in Cambodia.
In contrast to languages from neighboring countries like Vietnam, Thai, Lao, China, Khmer is a non-tonal language. This means that native Khmer words are stressed on the final syllable. The language system possesses a rich system of affixes, including infixes, for derivation even though it is uninflected. The normal word order is subject-verb-object, and adjectival modifiers follow the nouns they modify.
There are three stages of Cambodian language: Old Khmer (7th to 12th century A.D.), Middle Khmer (12th to 17th century A.D.), and Modern Khmer (17th century to the present). Nowadays, modern Khmer is widely used throughout the nation and is understood by most of the country’s inhabitants.
2. Minority Languages in Cambodia.
2.1. Cham.

There are about 220,000 Cambodians speaking Western Cham.
Cham is formerly the language of Champa Kingdom (from around the 2nd century AD until 1832) in Central Vietnam. This language is spoken by up to 220,000 people in Cambodia, and 100,000 people in Vietnam. In Thailand and Malaysia, there are also small populations of Cham speakers. Cham spoken in Cambodia is called Western Cham, whistle Eastern Cham language is used by people living in the coastal areas of Central Vietnam.
Like Khmer, Cham language belongs to the Austronesian family and is non-tonal. Words may contain one, two, or three syllables and as in Khmer, the normal word order of Cham language is subject-verb-object. Modifying adjectives also follow the nouns that they modify. Cham borrows much linguistic from Arabic, Malay, and Khmer.
2.2. Vietnamese.
Due to the geographical proximity, it’s no surprise that Vietnamese is a part of the Cambodia language system. Together with Khmer, Vietnamese belongs to the Austroasiatic language and has a long-established recorded history of more than 150 years. Vietnamese vocabulary is heavily influenced by Chinese with some 30-60% are naturalized word borrowings from China. As a result of French occupation and Western cultural influence, there are many new words added to Vietnamese’s lexicon. Generally, Vietnamese has a comparatively large number of vowels pronounced with an inherent tone.
Vienamese language is spoken in areas along two countries’ border land crossings, and where Vietnamese immigrants live in Cambodia.
2.3. Chinese.
Chinese is a popular language in Cambodia with the earliest records of Chinese settlement from the late 13th century. Chinese Cambodians are also known as Sino-Khmers. According to the official censuses between 2004 and 2008, Chinese consisted of 0.3% of the country’s total urban population and are concentrated mostly in Phnom Penh (about one-third of city’s population are Chinese).
Nowadays, young generation of Chinese Cambodians learns Chinese to reaffirm their Chinese identity. In addition, Chinese has become the primary language of business for overseas Chinese business societies with the rise of China’s global economic prominence. Cantonese and Mandarin are taught in Chinese-language schools in Cambodia.
2.4. Jarai.
The Jarai language is a member of Malayo-Polynesian branch of the Austronesian language family. It’s also related to the Cham language of Central Vietnam and Cambodia. There are around 335,000 people speaking this language. Jarai speakers make up 23% of the population of Ratanakiri Province in Cambodia. Being impacted by Khmer linguistic environment, few Khmer Jarai words are borrowed from Khmer and Lao. In addition, Jarai loses almost all vowel distinction in the initial syllable because it has developed in the pattern of the Mon-Khmer family.
2.5. Kuy.
Kuy language is a part of the Austroasiatic family so it’s not different from Khmer in appearance. Two main dialects in Kuy language system are identified in Cambodia with a relatively high degree of mutual intelligibility. Although Kuy is spoken mostly in northeastern Thailand and Laos, it also features among the northeastern provinces of Cambodia like Preah Vihear, Stung Treng and Kampong Thom. Kuy people’s villages are located in remote areas interspersed with Khmer villages.
2.6. Lao.
Lao language in Cambodia is a Lao-Phutai dialect of the Tai language family. Laos-Cambodians are also known as the Laotian Tai. Their residential places are mainly located along Mekong River and its tributaries, in the lowland regions of northern Cambodia.
2.7. Tumpoon.
Tumpoon belongs to the Bahnaric branch of the Mon-Khmer language family, and is closely related to Bhnar and Alak. It is spoken by the Tampuan people living in mountainous regions of Ratanakiri Province in northeast of Cambodia. There were 31,000 Tumpoon speakers according to the 2008 census, which equals to 21% of the province’s population at that time.
A script of Tumpoon was developed by a group of Cambodian government, UNESCO and NGOs in 1997 before it had not been written.
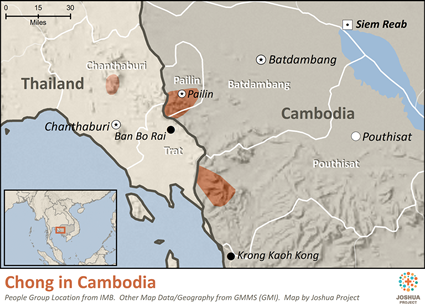
2.8. Chong.
Chong language is a Western Pearic language belonging the Mon–Khmer language family. This endangered language is now only spoken by Chong people in Pursat Province of Cambodia and in eastern Thailand. Historically, Chong people were cultivators and gatherer of cardamom and probably pre-dated the Khmers. Nowadays, only a few elderly people still speak this language, whereas younger people use Khmer only.
3. Foreign Languages in Cambodia.
3.1. French.
Among all Asian Francophone nations, Cambodia is the smallest French speaking community. French is spoken as a foreign language by 3% of Cambodia’s population in 2014. In 2008 census, there are only 873 Cambodian people spoke French as a mother tongue. Cambodian French is based on standard Parisian French and its vocabulary got influenced by Cambodian, Cantonese Chinese and Teochew Chinese.
This language was firstly introduced in Cambodia in the late 20th century after French explorers and merchants made their way from Vietnam into Cambodia. French was only limited to politicians because the French exerted considerably less influence on Cambodia as they did in Vietnam. Until the 1890s to 1910s, French was imparted in Cambodian education. And the language experienced significant growth until the Japanese invasion of Cambodia in World War II. French was used alongside Khmer in government as well as taught in schools. After Cambodia independence in 1953, this language continued to strongly present in the government and education.
In the mid-1970s, French had almost been completely eliminated from Cambodia because mostly French-educated Cambodians were killed by the Khmer Rouge. However, French was reintroduced when Vietnamese invasion established the People’s Republic of Kampuchea. Then French declined again when the current government of Cambodia was installed in 1993 and Khmer became the official language in Cambodia’s government and education system.
French and English are in the top 5 most commonly used foreign languages in Cambodia.
The revival of French language in Cambodia is stronger than in Vietnam and Laos. Because it’s still a diplomatic language of Cambodia nowadays. The French-speaking population of Cambodia consists of returned refugees from France and Quebec and who have studied in Francophone nations.
3.2. English.
Even French was the dominant foreign language in Cambodia, it took the decline and was replaced by English in 1993. Beginning in the late 1990s, English was widely taught in Cambodia because it was considered as the global language. Today, English is most frequently used across national boundaries. Due to globalization process of today’s world economy, Cambodia has recently transformed towards a market economy.
English is the language that this political context of Cambodia demanded and the study and use of English has been strongly encouraged and promoted. Cambodians can see themselves having a better life with better job and better pay if they have English education.
Visiting main tourist destinations in Cambodia, tourists can see that almost street signs and panels of restaurants and shops are usually written in Khmer and English. English is the most preferred foreign language in Cambodia with more job opportunities for English speaking Cambodians.
What is the official language of Cambodia?
Khmer, also known as Cambodian, is the most popular language in Cambodia and is by far known as the single official language and used in most social and professional contexts such as government administration, all levels of education, and social media.
What language can locals use to communicate with foreigners?
Apart from Khmer language as mother tongue, locals can communicate in English, French or Vietnamese languages.
What language is spoken in Cambodia?
There are 10 other languages widely spoken in Cambodia besides the official Cambodian language: Cham, Chines, Jarai, Kuy, Lao, Tumpoon, Chong, Vietnamese, Thai, French and English